Subscription growth hack (by PayKickstart)
Facebook Group - 3,932 members
Visit Group
Whether you currently run an e-commerce business, or you are in the processes of setting up one, there are some things you will need for your business to run smoothly. The first and most obvious will be an e-commerce website.
The second most crucial things you’ll need is a way to accept payments. Although you can ask people to send you money directly via PayPal or a wire transfer, this is not a scalable or safe option.
Instead, you will need to use a payment gateway backed by a payment processor, two parts of the entire e-commerce payments ecosystem.
In this post, we define each to help you understand how they work together to help your e-commerce business thrive.

The simplest definition of payment gateway comes from an analogy. In a physical store, the cashier accepts credit/debit card payments using a point-of-sale or POS terminal. This terminal has a card reader/swipe slot or a chip scanner.
By inputting your card details into the POS, the cashier can bill you and complete the transaction.
Think of a payment gateway as a virtual POS on your e-commerce store – one that allows your customers to make a card payment and complete a transaction.
Examples of payment gateways include PayKickstart, Authorize.net, 2Checkout, Amazon Payments, PayPal Payments, and Stripe.
The first and most important feature of a payment gateway is its security features. Without a payment gateway, your customers’ credit card information would be accessible to hackers, leading to instances of fraud.
A payment gateway encrypts users’ card details (and other details) via SSL encryption so that this information can be transmitted safely and securely to the payment processor (more on this later).
You’ll agree that there are dozens of ways to create an e-commerce store. Each of these methods introduces complexities to processing card payments. If the payment processor had to accommodate all these methods, e-commerce would be a very difficult business.
Payment gateways lift this heavy load by integrating with e-commerce platforms like Magento, WooCommerce, and others and creating a standardized way of sending payment details to payment processors.
Unlike a physical store, your e-commerce website stays open 24/7. A payment gateway automates the payment process allowing buyers to make purchases at any time.
This level of automation also makes it possible for your business to scale to thousands of transactions per day with no additional effort on your part.
Today, buyers want to make payments using credit cards, debit cards, gift vouchers, PayPal, wire transfers and a host of other methods.
Most reputable payment gateways support all these types of payments making it easy for your customers to pay using their preferred method.
In some instances, your e-commerce store may serve customers in other countries. Although most stores prefer to charge in US dollars and then let the issuing bank do the conversion, a payment gateway can allow you to charge using the user’s preferred currency.
As you run your e-commerce store, you’ll need to stay on top of all the transactions being made. Most payment gateways offer reporting features that include dashboard overviews, detailed exportable reports, and real-time transaction reports/notifications.
Payment gateways come with several costs that you should be aware of.
These include:

If a payment gateway acts as a virtual POS, the payment processor acts as an intermediary between the POS and the merchant bank.
The payment processor receives all the payment information (card details) transmitted by the payment gateway and passes this information on to the merchant bank.
Examples of payment processors include PayPal, Stripe, and Square.
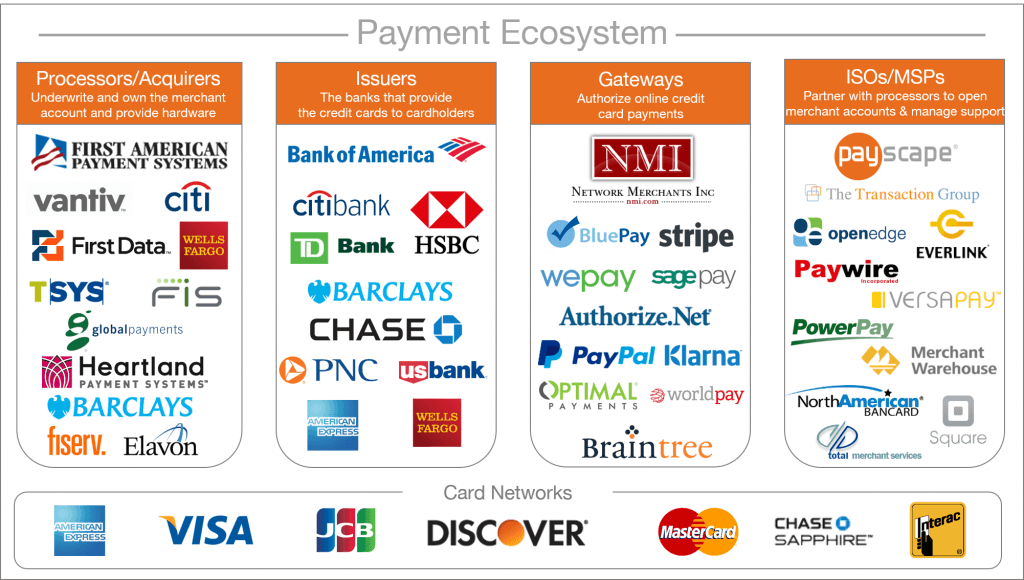
Before we discuss payment processors further, it’s important to make a distinction between three frequently interchanged and misunderstood terms.
Acquirer – this is the merchant bank or the bank where the funds from the transaction will be deposited. This party is responsible for ensuring money paid in is made available to the merchant.
Issuer – this is the bank that has issued the card being used to make the payment. This bank is responsible for forwarding funds to the acquirer (merchant bank).
Payments processor – this is an intermediary entity (not always a bank) that sends information to the acquirer or acquiring bank. It serves as a notification party alerting the acquirer that a transaction has been initiated and that the acquirer needs to settle the transaction.
Payment processors work with multiple payment gateways to consolidate transactions on behalf of merchant banks. In some cases, payment processors can also offer merchant bank services although most prefer to maintain partnerships with merchant banks.
When a transaction is initiated, payment processors are responsible for ensuring the transactions pass certain standards. For example, is the card number correct, has the card been blacklisted, does the payment meet certain security standards (like SSL encryption). Based on this, a payment can be declined before it reaches the merchant bank.
Because fraud is a major concern when it comes to e-commerce, payment processors invest a lot of resources in ensuring payments meet high-security thresholds. For example, if a card has been flagged, the payment processor will block all payments from that card from going through.
All payment processors must adhere to the standards set out by the PCI Security Standards Council. These security standards are set by members of the PCI SSC, who include organizations like MasterCard, VISA and American Express.
In most instances, a payment processor’s cost will be an amalgamation of various other costs charged by the issuer, acquirer, and even the credit card association.
Here is a breakdown of the costs:
In summary, a payment gateway acts as a virtual POS for your e-commerce store and the payment processor acts as an intermediary between your payment gateway and the merchant bank.
If you are looking for a payments solution for your e-commerce store, PayKickstart offers integrations with the top payment gateways like PayPal and Stripe, which also act as payment processors, offering an all-inclusive payments solution.
Sign up for a free PayKickstart trial today and find out how you can start accepting payments the easy way.
Dan Macharia is an experienced copywriter with over ten years of experience writing for both large and small companies all across the United States. When he is not writing, find him reading a book or outdoors playing lawn tennis, running or just walking and soaking in life.
Read More About Dan Macharia