Subscription growth hack (by PayKickstart)
Facebook Group - 3,932 members
Visit Group
Did you know that you can make a rough guess about how much consumers would pay for your products? Willingness to pay is the maximum amount of money a consumer would sacrifice in exchange for a product or service.
On the other hand, willingness to accept is the minimum amount of money an individual, a seller in our case, demands in exchange for a good. Meaning, both the consumer and the seller have different expectations from the transaction of a good or service. Only if one’s expectation coincides with the other’s, a transaction could happen.
A business can improve consumers’ willingness to pay. However, it can’t fundamentally change WTP. Some factors affecting WTP are beyond control. Furthermore, it’s an uncertain value that could change any time, even when it’s being measured. Then, what’s the benefit of measuring it?
For starters, it gives you an understanding of how consumers perceive the value of your products. If the general perception doesn’t overlap with what you’re trying to build, then there is something wrong with your marketing strategy.
More importantly, it’s an indicator of your future sales volume. Pushing a price tag much above consumer expectations can cause a significant drop in demand. Therefore, making a WTP assessment before setting prices would help you find the optimal price-demand ratio.
Before we proceed, it’s important to note that WTP is a contextual and personal measure. We won’t examine the effects of demographics, income, or situation of the economy on WTP although they certainly exist.
We’ll focus on factors that are relatively easy to measure and more open to improvement. Remember that these factors are also interactive, therefore, changes in one affect the other.
Consumers overly attribute price to quality. It means two things:
First, if the price of a product is too low compared to consumer expectations, its perceived quality will be poor. Competing on prices is a must for e-commerce businesses. However, extremely low prices make a store look like an online shopping scam.
Second, perceived quality could be changed in favor of an improved WTP. A business can (and should) work on improving the quality of its products, but for some products, development requires a lot of investment. In those cases, there is a second option.
Since consumers assume there is a strong relationship between price and quality, a brand can try to increase perceived quality by simply raising prices. But there is a risk to it. If the perceived quality is much lower than you anticipated, your tactic might backlash.
A safer tactic is using the decoy effect. The decoy effect can be described as the addition of an option that’ll reconstruct consumers’ perception of the original product.
Suppose you sell truffles.
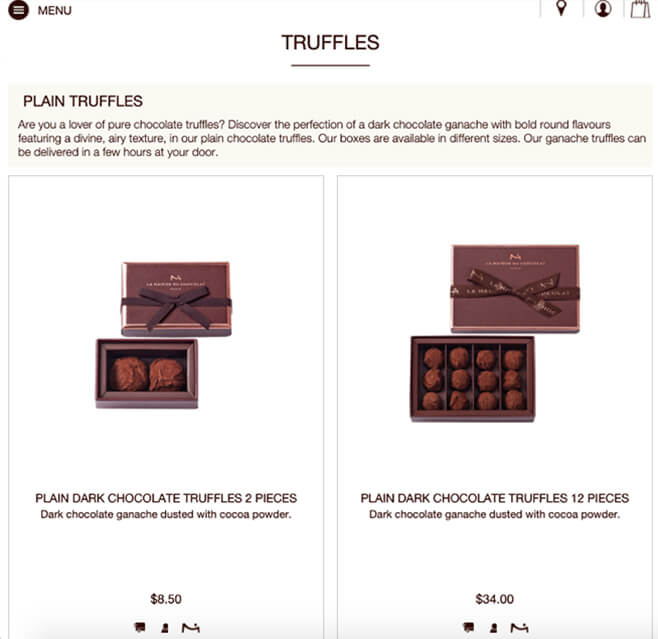
A decoy option would be 5 pieces of truffle sold on $25. Even if the quality remains unchanged, consumers become more willing to buy the $34 version.
Research on branding suggests that the image of a brand can dominate the quality of products under it. That means people don’t make individual quality assessments and trust the brand’s image.
Would you expect low-quality boots from Dr. Martens?
Doc Martens are known for their solidity. Consumers’ subconscious mind assumes each product under this brand is built to last forever. In cases where the product line is heterogenous, this assumption is highly likely to fail. Furthermore, as businesses expand and start outsourcing, it causes a reduction in the overall quality.
A study on consumer behavior revealed that a well-known brand name drastically increases the preference for the object. Researchers observed an 80% increase in the preference for a pair of shoes if the brand name is (ECCO) given.
We all know that exclusiveness makes a luxury product more attractive. Would Jay-Z wear a Rolex if it was for $2000? Just the satisfaction of owning a Rolex can make consumers’ WTP incredibly high. People emotionally benefit from products.
But it doesn’t have to be a high-end good. Don’t you have a friend that always talks about the importance of eating healthy? The person not only benefits from the product itself but also the feeling of healthiness.
Or, let’s go back to the times when Apple launched the iPhone. Everyone wanted to have an iPhone, and they were willing to pay a lot for it. But what happened to Apple’s market share in the past few years?
When an innovative product first enters the market, the company can sell it for the price they want, and early adopters will purchase it regardless of its price. However, in time, the competitors adopt the technology and develop substitute products with similar features.
In the 1976 issue of Harvard Business Review, economist Joel Dean talks about the three aspects of maturity in a product’s life cycle.
The first, technical maturity refers to the standardization of products among different brands. What does that mean? That means competitors catch up with the pioneer’s technology.
The second, market maturity refers to the widespread belief that all the products from different manufacturers will satisfy consumer expectations.
The third and last, competitive maturity refers to the phase where prices and market shares are stable.
In 2007, Apple released the iPhone at the price of $599. Before others adopted the iPhone’s technology, Apple dominated the market.
Then, the product reached a certain level of technical and market maturity. In this phase, price elasticity of demand increases. Normally, when the competitive edge is lost, companies shift the marketing strategy toward competing on prices. But Apple didn’t.
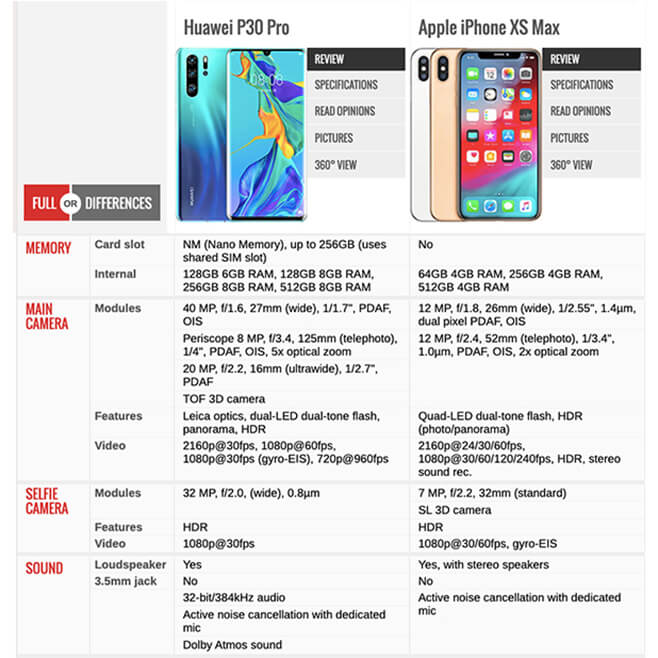
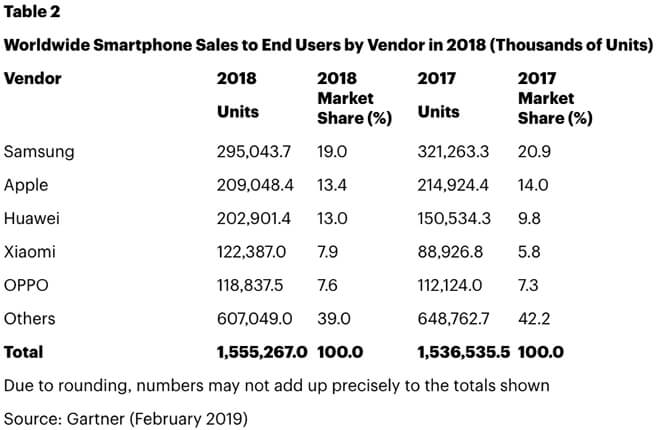
Now, the company’s market share is declining (along with Samsung’s) while Huawei and Xiaomi are expanding. Depending solely on branding doesn’t sustain a high WTP. This year, Apple released its entry-level device iPhone 11 for $700, $50 less than the product it replaces as an effort to offer more competitive prices.
People hold price knowledge from their past experiences and construct reference price points. When they see a new product, they check back with these reference points and decide upon a ‘fair’ price. Marketers try to raise these reference points by exposing consumers to high anchor prices.
Research on price perception shows that even irrelevant anchor prices can change reference prices. Scholars found out that using a Mercedes price as an anchor to a Buick car works. These brands do not compete with each other, but the exposure to one’s price affects WTP for the other.
Businesses can measure WTP with four different tactics knowing the fact that they all have advantages and disadvantages.
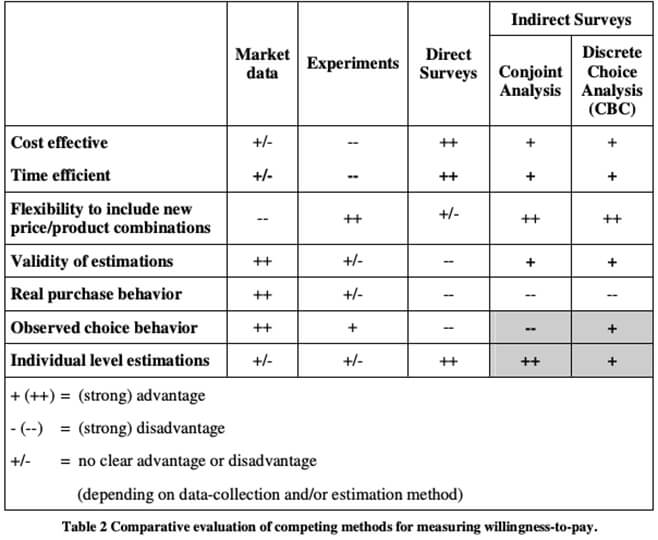
Analysis of other players in the market, demand, price changes and all the relevant secondary data to estimate WTP. You can track most of these with pricing software.
Simulating a purchase environment by giving money and providing different options to a consumer group.
Observing consumer behavior in real-life shopping scenarios (in-store).
Sales or marketing experts estimate consumer demand based on their knowledge on the competitive landscape.
Asking customers their willingness to pay.
Presenting consumers many different products with various prices and ask them to rank order their preferences. The results are analyzed via several methods to derive a general estimate for the market.
Having willingness to pay knowledge for a product can give you a clue about the relationship between price and demand. Although it suffers from uncertainty problem, businesses can make estimates of WTP. There are 5 factors affecting WTP; perceived quality, brand image, emotional & self-expressive benefits, alternatives for the product, and reference prices. These factors can be improved.
To measure WTP businesses can:
All of these methods have advantages and disadvantages and businesses can choose one depending on their needs.
Basak Saricayir is the content marketer at Prisync which helps E-commerce companies increase sales by tracking prices automatically from any marketplace around the world.
Read More About Basak Saricayir